RFID
Radio Frequency IDentification (RFID) is a method of Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC). UHF RFID uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags that are attached to objects.
The chip can be encoded with the tag’s ID and information about the object it is attached to. The chips in the tags are very small; almost invisible when incorporated into products. Multiple chips can be read at the same time. This makes RFID technology ideal for tracking, tracing and data collection.
Frequencies
RFID operates on three radio frequencies: low, high and ultra high. Ultra High Frequency (UHF) RFID operates in the 300 MHz to 3 GHz range. It is the same frequency used by telephone and broadband networks, making it an ideal technology for setting up or connecting to an Internet of Things environment.
Active versus Passive
Active tags have their own energy source and can autonomously transmit signals over distances from 100 meters up to several kilometers. Passive tags do not have batteries; they rely on RFID readers to be able to transmit signals. Their maximum reach is approximately 8 meters. They are most often used for indoor solutions, active tags are usually operated outdoors.
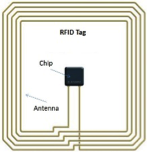
Example A:
UHF RFID tag

Example B:
UHF RFID tag
Like to know more?
Contact us!